I moved to a new location last week, so I changed my address on Bloomberg’s website. Now I will receive the new issues of Bloomberg Businessweek magazine at my new address.
The same principle applies to websites, so If you change the URL of a web page, you need to let your visitors and search engines know where to find it. This is where we use redirects like 301.
A 301 redirect is a way of telling browsers and search engines that a page has permanently moved to a new URL.
In this article, I will explain what are wordpress 301 redirects, when to use them, how to use them, the SEO effect of the redirect, and some common mistakes to avoid when using 301 redirects on your wordpress website.
What is 301 Redirect and How Do they Work?
A 301 redirect is a way of telling web browsers and search engines that a web page has moved to a new location permanently. It preserves the traffic, ranking, and user experience of the old page by automatically redirecting visitors and bots to the new page.
For example, suppose you have a blog post with the old URL https://example.com/blog/seo-tips and you want to change it to https://example.com/blog/seo-best-practices.
You can use a 301 redirect to ensure that anyone who clicks on the old URL will be taken to the new one seamlessly.
The 301 redirect works by sending a message to the browser or the search engine that the page they are looking for is no longer available at the old URL and that they should go to the new URL to find it. The browser or the search engine then updates their records and caches the new URL for future requests.
When to Use 301 Redirect?
Different types of redirects, such as 301, 302, 303, and 307, are used for different scenarios. Knowing when to use which redirect can help you improve the SEO of your site and avoid negative effects on your website but before finding out how to use the 301 redirect let me clarify the difference between the 301 and 301 redirect.
301 vs 302 Redirect
When you want to change your website’s URL, you can do that by using a 301 redirect or a 302 redirect these two type of URL is most commonly used.
A 301 redirect means that the old URL is gone for good and that the new URL is the permanent replacement. Search engines will update their index with the new URL and browsers will cache it. This way, your visitors will always see the new URL and your SEO will not be affected. You should use a 301 redirect when you change your domain name or URL structure, or merge two websites.
A 302 redirect means that the old URL is still valid and that the new URL is only a temporary alternative. Search engines will keep the old URL in their index and browsers will not cache the new URL. This way, your visitors will see the new URL only for a short time and your SEO will not be changed. You should use a 302 redirect when you test a new page, perform maintenance, or temporarily move your content.
Choosing the right redirect is important for your website’s performance and user experience. If you use a 301 redirect for a temporary change, you might lose your original URL from search results and confuse your visitors. If you use a 302 redirect for a permanent change, you might create duplicate content issues and lower your rankings.
Moving Page Permanently to new URL
I have used a 301 permanent redirect many times on my own website. It helps me keep my site updated and user-friendly.
For example, when I changed the URL of my blog post.
From https://www.webtalkhub.com/remove-url-from-google-search/ to https://www.webtalkhub.com/remove-url-google/.
I used a 301 permanent redirect to avoid losing any traffic or SEO power. This way, anyone who visits the old URL will automatically be redirected to the new one.
A 301 permanent redirect is a simple and effective way to change the URL of a page without affecting its performance or ranking.
Deleting a Page on a Website
Sometimes, you may need to delete a page on your WordPress website. However, this does not mean that the page will disappear from Google’s index right away. If someone tries to visit the deleted page from a search engine, they will see a 404 error page like this:
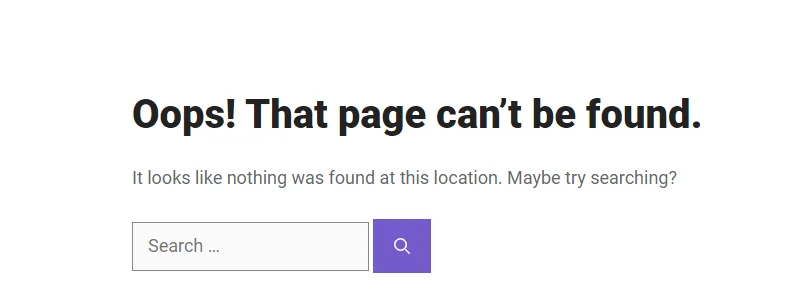
This is not a good practice and can affect the user experience negatively. Instead of showing the user a 404 page, you can 301 redirect the deleted page to another relevant page on your site that matches the user’s intent.
This will improve the bounce rate on your site, as the user will not be frustrated with the default 404 page and will explore your other site pages instead.
Also for a more user-friendly approach, you can check our guide on creating a custom 404 page in WordPress for a more user-friendly approach.
Changing your Website Structure
If you want to change your website structure to better organize the content and to make it easier for Google to understand, you can use a 301 redirect in this scenario.
For example, if your current site structure is https://www.website.com/blog/post/ and you want to change it to https://www.website.com/blog/category/post/, you can use a 301 redirect to redirect the traffic and the ranking signals from the old URL to the new URL.
This is especially recommended for e-commerce websites and other large websites that have a lot of content and need a clear and logical structure.
Migrating your Website to a New Domain
A 301 redirect can be used when migrating your wordpress site to a new domain.
For example, you can redirect https://www.oldomain.com to https://www.newdomain.com.
This way, you can keep the authority and power of your old domain and rebrand your site with ease. You should also tell Google about the domain change for your website, as this will help you update the search results faster.
Changing From HTTP to HTTPS version
Use 301 redirects to move your website from HTTP to HTTPS, which is more secure and Google-friendly.
For example, redirect.http://www.mywebsite.com to https://www.mywebsite.com. This keeps your traffic and ranking signals.
Also, HTTPS is also recommended by Google for websites and it is a ranking signal for Google, meaning that it can improve your website’s visibility and trustworthiness in the search results.
A 301 redirect makes it easy to switch from the HTTP version to the HTTPS version of your website, without losing any traffic or ranking signals.
You can also check out our detailed guide on redirecting HTTP to HTTPS for a smooth website transition.
Switching from Non-WWW to WWW URLs (Fixing Duplication Issues)
A 301 redirect is the best option if you want to switch from the www version to the non-www version of your website.
For example, if your website URL is https://www.yourwebsite.com and you want to move it to https://yourwebsite.com, which is a cleaner URL, you can use a 301 redirect to do that. This way, you can avoid the duplicate content issue, which is bad for your website’s SEO.
A duplicate content issue occurs when the same content is available on multiple URLs, which can confuse the search engines and lower your rankings.
By using a 301 redirect, you can tell the search engines that the non-www version is the preferred one and that they should ignore the www version.
Combining Multiple Domains
A 301 redirect is a way to combine two or more domains into one.
For example, suppose you have two domains for your site: https://mybusiness.com and https://mybusiness.nl. You want to merge them into https://mybusiness.com/nl/. You can use a 301 redirect to send the traffic from the .nl domain to the .com domain.
However, before you do that, you need to plan carefully how to combine the two domains for your business to preserve the SEO of the website.
Solving ‘Trailing Slash’ Problems
A 301 redirect can be used when your site has a trailing issue and Google treats pages with and without a trailing slash differently.
For example, https://www.mywebsite.com/page-1 and https://www.mywebsite.com/page-1/ are considered as two separate pages by Google.
To fix this issue, you can use a 301 redirect to make your site consistent in handling the permalink. This means that whenever someone visits a page with a trailing slash, they will be automatically redirected to the same page without a trailing slash, or vice versa.
Fixing Upper-Case and Lower-Case Problems
Google is case-sensitive when it comes to URLs. This means that using upper-case and lower-case letters in your permalink can make a difference.
For example, https://www.mywebsite.com/Page-1/ and https://www.mywebsite.com/page-1/ are not the same pages for Google.
This can cause a duplicate content issue in your search console, which can affect your site ranking in Google SERP. To solve this issue, use a 301 redirect.
This will make sure that all your pages have a consistent case in their URLs. For example, you can redirect all the pages with upper-case letters to the same pages with lower-case letters, or the other way around.
How to Use 301 Redirect in WordPress
To do a 301 redirect in WordPress, you will need to install and activate the Redirection plugin by John Godley. You can find this plugin by going to Plugins > Add New and searching for “Redirection”. The plugin has a featured image as shown below:
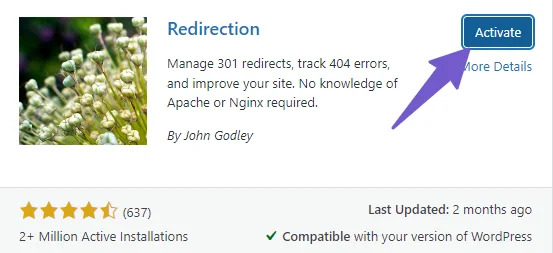
After activating the plugin, go to Tools > Redirection in your WordPress dashboard. You will see a setup wizard that will guide you through the plugin settings. Just click next until you finish the setup.
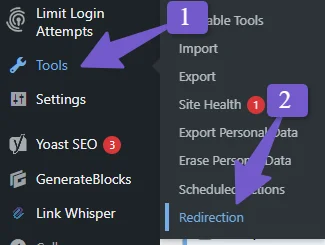
Now you are ready to add your redirections. In the Source URL field, enter the old URL that you want to redirect, for example https://mydomain.com/example-post-1/. In the Target URL field, enter the new URL that you want to redirect to, for example, https://mydomain.com/post-1/.
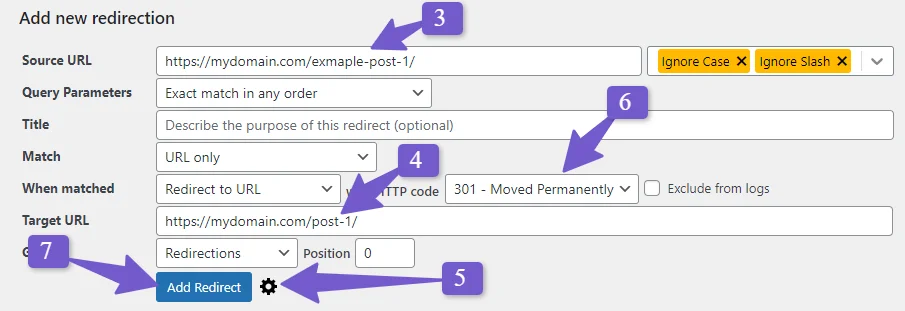
You can also click on the gear icon to open more options, such as choosing the type of redirect. But 301 redirect is already selected so we can leave this option Then click on the Add Redirect button at the bottom.
The plugin will also monitor the 404 errors on your site, which you can then manually redirect. There are also more advanced features that you can explore if you want to create more complex redirections.
For more advanced features and to explore complex redirections, check out our guide on the best WordPress redirect plugins.
If you are interested in other methods of implementing 301 redirects, you can check our detailed guide on WordPress redirects. It provides an in-depth overview, serving as a central resource for all your redirection needs
Common Mistakes with 301 Redirects and How to Prevent Them
301 redirects if not implemented correctly, can cause some issues for your site’s SEO and performance. Here are some common mistakes with 301 redirects and how to prevent them:
Using 302 Instead of 301 Redirects
Many SEOs make the common mistake of using a 302 instead of a 301 redirect because they don’t know the difference between them.
A 301 redirect is used when the URL change is permanent, and a 302 redirect is used when the change is temporary.
For example, suppose you have a product page with the URL https://www.example.com/products/product1 and you want to redirect it to a special offer page with the URL https://www.example.com/special-offer for a limited-time promotion.
In this case, you should use a 302 redirect to tell both web browsers and search engines that the change is temporary and that the original URL will be restored after the promotion. This way, the search engines will still use the original URL to rank the product in the SERP and the URL will not lose its SEO value.
However, if you use a 301 redirect in this case you will tell the web browsers and search engines that the URL is permanently redirected and that the original URL is no longer valid. This can affect your SEO ranking and traffic negatively. Therefore, you should always use the appropriate redirect type for your situation and remember that 301 and 302 redirects are different.
Redirecting to Irrelevant pages
If you redirect a page to a new URL that is not relevant or similar to the original one, you can lose the trust and interest of your visitors and search engines.
If you redirect a page about shoes to a page about hats, you are not providing a good user experience or satisfying the user intent you can check the example below.
From https://example.com/product/shoes to https://example.com/product/hats
To prevent this, you should redirect a page to a new URL that has the same or similar topic, content, and keywords as the original one you can check the example below.
From https://example.com/product/shoes to https://example.com/product/leather-shoes
Redirect Chains & Loops
Redirect chains and loops are one of common mistakes with 301 redirects. A redirect chain is when a page goes through more than one redirect before reaching the final destination.
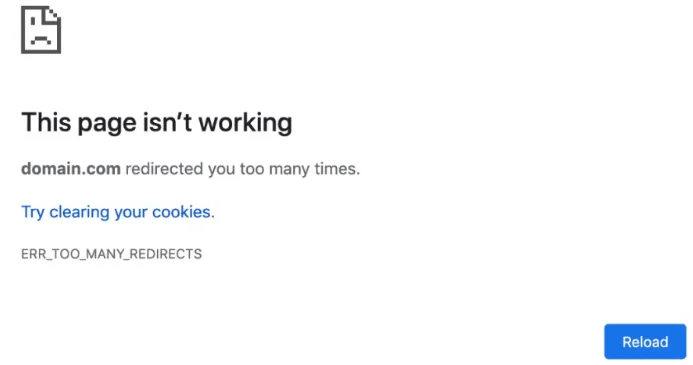
A redirect loop is when a page redirects to itself or to another page that redirects back to it. Both of these scenarios can cause slow loading time, poor user experience, and loss of SEO value.
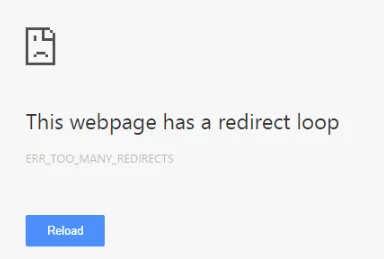
To prevent redirect chains and loops, you should use as few redirects as possible and avoid circular or unnecessary redirects.
You can also use the Ayima Redirect Path extension to help you analyze your redirects and show you the path of the redirect. If the extension detects any error on the page, it will turn yellow and you can check and fix the redirect issue if any.
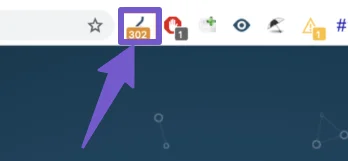
Moreover, if you have Ahrefs or SEMrush, you can use their audit tools to find the redirect chains and loops for your entire website.
Not Updating External and Internal Links
If you redirect many of your pages, it will trigger many redirects as the original page you redirect might have many internal links and external links pointing to it.
To avoid this, you have to update all the internal and external links pointing to the old URL that is redirected.
For internal links, you can use Google Search Console to find the internal links for the page you want to redirect. Go to your Google Search Console and then go to Links in the right sidebar. There you will see the Internal Links menu. Click on it and find the page that you are redirecting. Click on it and it will show you all the internal links pointing to this page.
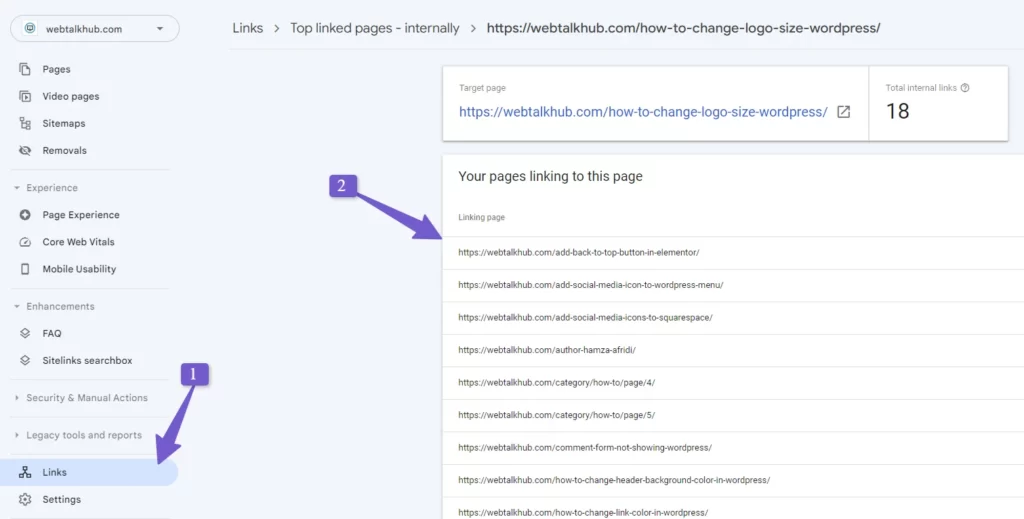
You can export them as an Excel or CSV file and later update all the pages with the new redirect URL. This will not load the site and the internal links will point to the new page directly, avoiding a chain of redirects.
For external links, go to the Links in Search Console and now go to the External Links menu. There, find the page that you have redirected and click on it.
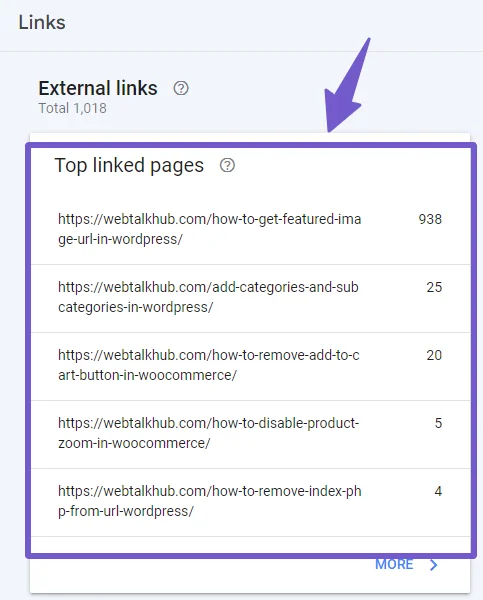
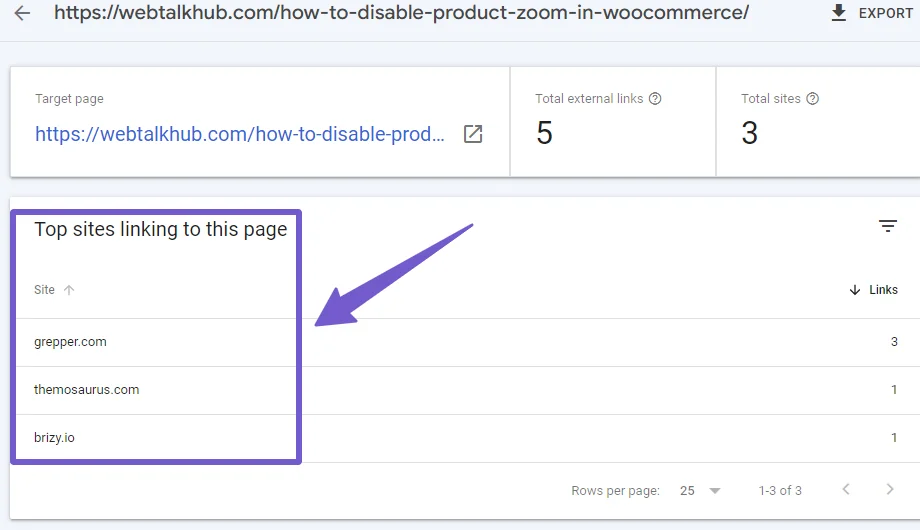
Reach out to the owners of websites that have high domain authority and ask them to change the link to the new page URL.
You cannot reach out to all the external link sites, but at least if the top backlink sites change their links and point to your new URL, it will help in SEO.
Not Testing Your Redirects
One of the major mistakes that many people make is not testing their URLs after implementing redirects. This can result in broken links, redirect chains and loops, and other errors that can harm your site’s performance and SEO.
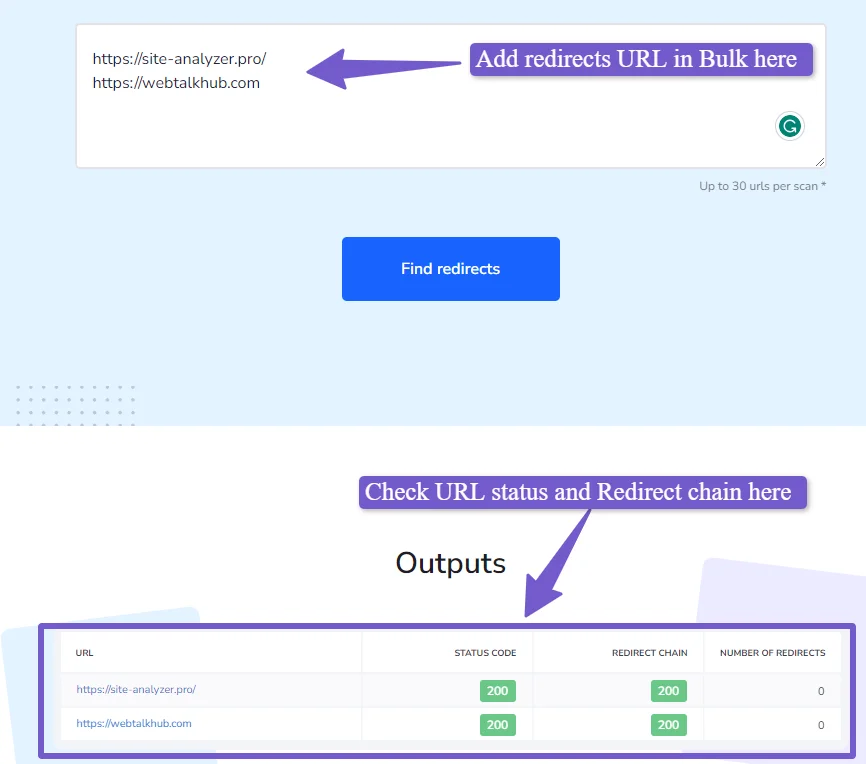
To prevent this, you have to manually test the redirects after implementing them and monitor them regularly for any issues.
You can check all the redirects you have in bulk by going to an online redirect checker and it will give you the 200 status code for OK URLs.
Not Updating your Sitemap and Robots.txt
If you have redirected a large portion of your website content using the 301 redirects and didn’t update your sitemap and robots.txt, then you are making a major mistake. This can slow down the redirect process and also cause errors. Also, the search engines will not easily crawl and index your site’s new updates.
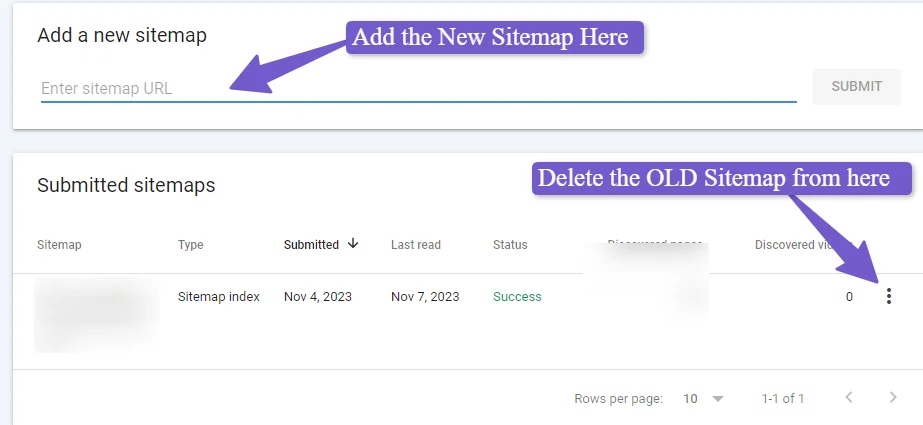
But how can you update the sitemap and robots.txt? Well, in WordPress, it is really simple if you are using an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math SEO. They have separate options for Sitemap Settings. Go there and click on Save Changes. It will generate a new sitemap.
After that, you have to go to your website’s Search Console remove the old sitemap, and submit the new one. This way, Google will crawl the new sitemap fast and you will be fine with the redirection of a large site. The same you have to do for other webmaster search consoles like Bing etc.
If the page that you made a 301 redirect for is blocked from robots.txt or maybe its folder, then you have to modify your robots.txt file as well. If not, you can skip this step.
For the robots.txt file, if your SEO plugin has an option to modify it, you can do that in the plugin. If not, you can access your robots.txt file from the cPanel from your hosting in the File Manager and in the root folder, which is public_html. There you will find the robots.txt file, which you can modify.
SEO Impact of 301 Redirects: Optimizing Your Website Search Rankings
301 redirect impact on website SEO is discussed below and how you can use the 301 redirect in improving your website search ranking.
▶ Preserving SEO Value:
Example: You update your product page URL from https://www.example.com/product/shoes to https://www.example.com/product/running-shoes. Using a 301 redirect here you maintain the SEO authority and ranking of the old URL and the search engine will treat the New URL with the same authority.
Example for Preserving SEO Value:
Let’s say you run an e-commerce website, and you decide to update the product category structure. Previously, you had a category for “Electronics” with products like smartphones and laptops. You’ve now decided to create separate categories for “Smartphones” and “Laptops” for better organization.
Old URL: https://www.example.com/products/electronics/smartphone
New URL: https://www.example.com/products/smartphones/smartphone
By implementing a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one, you ensure that the SEO value associated with the “Electronics” category is transferred to the “Smartphones” category, preserving rankings and authority. This way, your website maintains its visibility in search results for smartphone-related searches while providing a more user-friendly structure.
▶ Maintaining User Experience:
Example: You restructure your blog’s categories, moving articles from https://www.example.com/blog/category/technology to https://www.example.com/blog/category/gadgets. so using a 301 redirect here will improve the user experience as they will find the not encounter error and will spend more time on your website which is an SEO factor.
Example for Maintaining User Experience:
Imagine you run a travel blog, and you have decided to reorganize your content by creating specific destination categories. Previously, all your articles were under a generic “Travel Destinations” category. You want to make it easier for your readers to find content related to specific cities.
Old URL: https://www.travelblog.com/destinations/paris-travel-tips
New URL: https://www.travelblog.com/destinations/paris/travel-tips
By using a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one, visitors looking for Paris travel tips can smoothly transition to the updated URL structure which will improve the user experience as well as the SEO of website.
▶ Avoiding 404 Errors:
Example: You delete a product page that had a high number of backlinks pointing to it. Instead of leading visitors to a dead-end with a 404 error, a 301 redirect takes them to a relevant, active page, preserving both user experience and SEO value.
Example for Avoiding 404 Errors:
Suppose you run an online store, and you decide to discontinue a product in your inventory due to low demand. The product’s URL is:
Old URL: https://www.examplestore.com/products/discontinued-product
Rather than showing visitors a “404 Not Found” error to users when they access this page, you can set up a 301 redirect to send them to a relevant product category or a similar product preserving the SEO of the old URL and improving the user experience.
▶ Handling Domain Changes:
Example: You migrate your website from olddomain.com to newdomain.com. 301 redirects ensure that the SEO equity from the old domain is transferred to the new one, preventing a significant loss in search engine rankings.
Example for Handling Domain Changes
If you want to rebrand your website and change its domain name from oldbrand.com to newbrand.com.
This can impact your site’s SEO if you don’t do it properly. By implementing a series of 301 redirects from the old domain to the new one, you ensure that search engines and users are directed to the new brand’s website. This maintains your search engine rankings and prevents a drop in organic traffic.
▶ Consolidating Content:
Example: You merge two blog posts on a similar topic. Redirecting the old URLs to the new, consolidated post not only maintains SEO value but also provides a better user experience with a single, comprehensive resource.
Example for Consolidating Content
You are running a tech blog and have written several articles on the latest smartphone models. So you want to provide a better user experience and want to merge the article on different smartphones into one comprehensive guide as shown below.
Old URLs:
https://www.exampleblog.com/smartphones/iphone12-reviewhttps://www.exampleblog.com/smartphones/samsung-s20-comparisonhttps://www.exampleblog.com/smartphones/pixel-4-features
New URL: https://www.exampleblog.com/smartphones/best-smartphones-guide
You use 301 redirects to send all the traffic and SEO value from the old URLs to the new URL.
▶ Evolving Content:
Example: You frequently update your ‘Best Practices for SEO’ guide. Each update is represented by a different URL. Using 301 redirects when you publish the latest version ensures that users and search engines always access the most current information.
Example for Evolving Content
You run a digital marketing website and you regularly update your most important and useful guide on “Social Media Advertising Best Practices.” Each update gets a new URL with the revision number.
Old URL: https://www.example.com/social-media-advertising-best-practices-v1
New URL (latest update): https://www.example.com/social-media-advertising-best-practices-v2
You use 301 redirects here to transfer all the SEO value and traffic from the previous URL to the latest URL.
FAQ (301 Redirect)
Below are some most common FAQs on 301 redirects.
What does a 301 redirect do?
A 301 redirect is a way of telling web servers to send users and search engines from an old URL permanently to a new one. It makes sure that when users type or click on the old URL, they are automatically taken to the new URL, without any interruption or confusion.
What are 301 and 302 redirects?
A 301 and 302 redirect have different roles in managing a website. A 301 redirect means that a page has changed its location for good, and it makes sure that all users and search engines know that the change is permanent. On the other hand, a 302 redirect shows that a page has moved to a new location, but it’s only for a short time, and the original URL should be used to index it.
Is 301 or 302 better for SEO?
Both 301 and 302 redirects can help users find the right webpage, but they have different effects on search engine optimization. A 302 redirect tells a temporary page change, while a 301 shows a permanent switch to a new page and tells the search engine to transfer the link equity and authority of the old page to the new so from an SEO perspective 301 is better.
Conclusion
In this guide, you have learned what a 301 redirect is, when you should use it, how to implement it correctly, and what are the common mistakes to avoid in 301 redirections. You have also learned how a 301 redirect can affect the SEO of your website.
I hope that this comprehensive guide has cleared all your confusion and ambiguity about 301 redirects. Now you have all the required information if you are planning to either transfer your domain or merge your site for better search ranking.
If you have any questions, you can ask me in the comments and I will assist you further. Thank you for reading.
